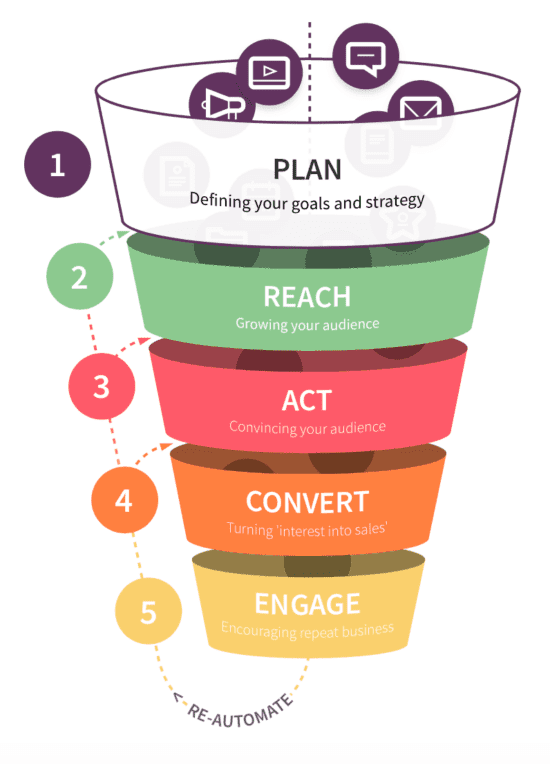
Why Create A Business Marketing Plan Today?
One of the most effective ways to reach your target market is to promote your business online. It is, however, possible that your online efforts may not succeed without a properly developed business marketing plan.
Marketing plans are utilized by many successful companies as a tool to implement their marketing strategies and to track the progress of all activities. In the following sections of this article, we will discuss how proper planning generally involves setting goals, creating buyer personas, performing an analysis of your competitors, identifying key performance indicators, and developing an action plan, as well as methods to review your ongoing results so you can track your progress.
The purpose of this article is to help you to understand what your marketing plan should include and why.
A business marketing plan is essential for an effective online promotional campaign.
A marketing plan will help you to identify and clearly understand your audience, measure your progress, and allow you to make any adjustments as they may become necessary.
In general, marketing plans have multiple functions. They assist businesses in
- Streamlining and organizing all marketing efforts
- Guiding businesses and their marketing teams through a series of activities
- Determining how to measure a campaign’s success and need for improvement
They also help organizations to efficiently and effectively create and allocate campaign budgets.
Start your marketing plan by selecting a few broad, general and achievable goals.
The specifics of a marketing plan, including the action steps, are typically filled in as the plan is being developed and revised. So don’t get held up at the beginning if you feel you haven’t yet identified all of the details. Once you’ve created your initial draft of the marketing plan, you can always modify the marketing plan by adding more specific goals, detailed steps, timelines, budgets, etc.
For example, an organization might decide to launch a new product or start a new promotion for a product or service. Here are some examples of a few initial and general goals you might use to start your marketing plan.
- Select a new product or service to launch.
- Reaching new potential clients through social media advertising, email campaigns, print media, radio, podcasts, or television broadcasts.
- Attract new visitors to your website.
- Increase sales of a specific product or service by XX%.
- Acquire XX, XXX, or XXXX new customers within the next XX days.

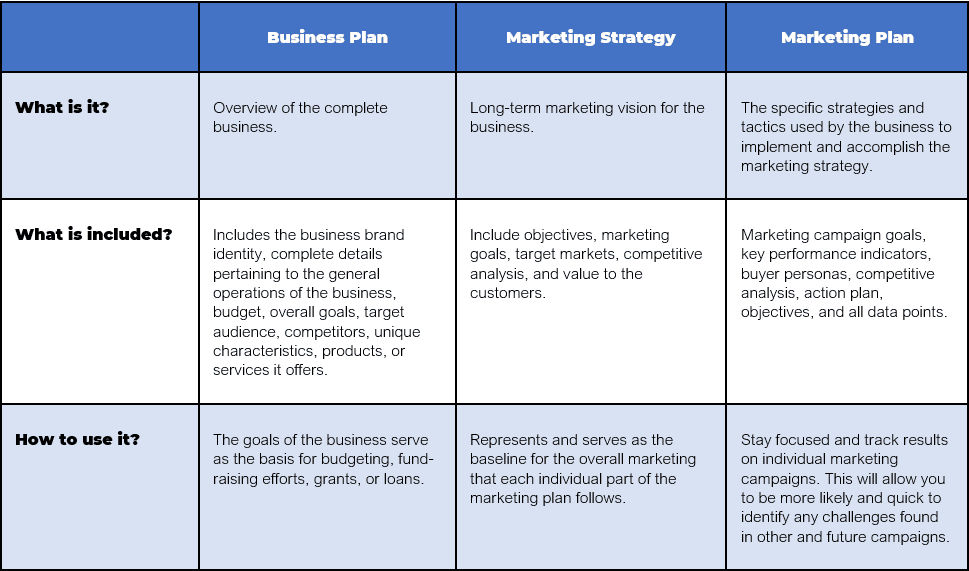
It’s important to understanding the differences between a marketing plan, a marketing strategy, and a business plan.
- A marketing plan is the promotional and advertising strategy that will implement to sell its products or services.
- A marketing strategy helps a business achieve its goals by understanding the needs of the customers and creating a distinct competitive advantage.
- A business plan describes a company’s goals and the course of action it will take to reach them.
While developing a marketing plan, you may run across similar concepts that are also found in your marketing strategy and business plan. Consider all three plans as written roadmaps for outlining your overall business. You’ll find similarities among them, including your business goals and information on your target market, but there are some important differences to be aware of as you construct these roadmaps.
While developing and reviewing your roadmap for each of these plans, be sure to keep an eye on the effectiveness of your marketing efforts, your budget, and your business overall.
Creating a Marketing Plan
Before creating a marketing strategy, outline your goals and the way you intend to attain them and include this within your marketing plan.
The following sections provide an overview of the steps to creating a marketing plan and the components of each phase. Start with the first one and work your way through each phase. As you complete each phase, review the information in each section that may need to be refined before continuing on to the next phase.
1. Executive Overview
- Here, you will write a short description for each of the sections that follow, usually no longer than a few paragraphs each.
- Details about the company’s mission, achievements, potential obstacles, as well as its brand identity.
2. Goals of The Marketing Campaign.
Summarize the marketing campaign’s goals and state them clearly. Here are some examples of broad and general goals.
Examples of Marketing Goals:
- The goal of this process is to get more email subscribers during the next quarter by increasing email subscribers by 50 percent within the next XX months.
- Increasing online purchases could be described as driving more traffic to a page that sells more products through social media advertisements. The conversion rate for sales from the website should increase from XX to XXX percent.
3. Key Performance Indicators, otherwise known as KPIs.
In order to determine whether your marketing strategies are effective, you will need to specify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs *). Tracking KPIs will allow you to constantly improve your outreach and steer your campaign toward success.
* Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure the performance, efficiency, results, accomplishments, etc., of a person, organization, or activity based on an expected target or goal.
Examples of Key Performance Indicators include:
- Increase the number of individuals visiting the company website by XX%.
- Obtain XXX new and additional email subscribers by XXX by XX/XX/XXXX (date).
- Achieve XX attendees at an event (i.e., potential customers).
- The rate at which leads are converted into customers (revenue figures) increase by XX% compared with the same time period from the previous year.
You should take note that these KPI examples are measurable. This is an important aspect of any KPI.

4. Customer Personas
Buyer or customer personas are fictional characters developed by companies to represent their actual or potential customers.
As you develop your marketing strategy and business plan, develop and study your buyer personas in detail. Focusing on your buyer or customer personas can help improve your marketing performance and drive campaign success. Communication with your customers is more likely to be successful if you can clearly and thoroughly identify and understand them.
Here are some of the things you’ll want to know about your customers.
- Personal characteristics such as their approximate age, income, location, occupation, etc.
- What do your customers do when they want to find products or services similar to yours? (How do they go about getting this information.)
- What keywords do they use to search for it?
- How do they prefer to purchase products and services? (Online, In-Store, At-Home, etc.)
- At what times of the day are they most likely active on social media or other marketing channels, online or offline?
Be sure to customize every aspect of your marketing campaign according to your target audience and help you and potential customers take action, such as subscribing to your email list or making a purchase.
5. PREPARE A Comparison Model of YOUR Competitors.
If you want to uncover insights about how competitor brands are reaching customers in your target market, follow your marketing strategy and business plan. Then, assess their marketing strategies in more detail. Look at what your competitors are doing and how.
There are several ways to obtain information about competitors:
- To attract an audience, use free and/or paid SEO (Search Engine Optimization) tools to inspect your competitors’ use of popular keywords, content, and advertising copy.
- Observe what content your competitors post on their social media networks to attract followers and identify the amount of engagement, shares, likes, etc., that each post obtains.
- Subscribe to your competitors’ emails to learn how they market and sell their products or services to potential customers.
6. Identify Action Items YOU PLAN TO IMPLEMENT AND WHEN
Marketing your products and services to customers requires identifying the strategies and methods you’ll employ in your marketing strategy and plan.
Insert a list or table of actions into your marketing plan document:
- The budget, start date, and end date of each campaign.
- Track your progress towards the campaign’s goal until the deadline is reached.
- The milestones you will need to pass in your project to reach each of the goals. (Milestones help you to stay on target at midway points during individual campaigns.)
- The offline and online marketing channels you plan to use.
- The schedule for implementation of each action step.
7. The Science of Analyzing and Testing Results
Your marketing plan should tell you how you will monitor KPIs and analyze your campaign results at each stage. Again, setting and using milestones will help with this process. That way, you will learn how to adjust your plans accordingly and determine what s working and what s not working.
Set up analytic tools for your social media accounts, website, email system, landing pages, and also your registration pages for events. Set calendar reminders that follow your business plan for reviewing KPIs.
Develop a team of individuals who will be responsible for monitoring the analytics. Weekly or bi-weekly meetings to review the data are often advised. Despite the fact that you can meet monthly or even quarterly, it’s best to meet more frequently and adjust the marketing plan as quickly and efficiently as possible.
- Which marketing methods are attracting the most traffic?
- Which marketing methods are converting at the highest rates?
- How are individual pieces of content performing?
- How efficiently is your budget performing?
- Which metrics are improving, staying the same, or declining over time?

Useful guide to setting SMART goals.
Many business professionals recommend the SMART system as a helpful and efficient method to set goals for your business marketing plan. Here is a SMART GOALS – MARKETING PLAN CHECKLIST. (Acrobat – PDF Document)- The lack of consensus on what constitutes success often prevents teams from accomplishing their goals.
- By using SMART goals, you can ensure that your objectives are clearly defined, measurable, and achievable.
- By working through each step of creating a SMART goal, you can identify areas where priorities and resources are out of alignment.
What is a SMART goal?
As an acronym, SMART goals stand for “S” Specific, “M” Measurable, “A” Achievable, “R” Relevant, and “T” Time-Bound goals. To ensure that you can accomplish your goal within the timeframe you have set, you need to define these parameters. By establishing a clear timeline, identifying missed milestones, and eliminating generalizations, this approach eliminates generalizations and guesswork. SMART-goal statements may look something like this: Our goal is to [quantifiable objective] by the [timeframe or deadline]. By [taking the steps necessary to achieve the goal], [key players or teams] will reach this goal. The results of achieving this goal will [benefit or result].We will work through each component using Margaret’s objective.
S: Specific
Specificity is essential to making a goal effective. The purpose of a specific goal is to answer questions such as:- Are there any tasks that need to be completed?
- Who’s responsible for each task?
- In order to achieve the goal, what steps will be required?